1. Hardwire a PC or connect via Wi-Fi to the Home Networking modem.
2. Launch a web browser, such as Microsoft Edge, Firefox, Chrome, Safari etc. Type 192.168.0.1 into the address bar and press Enter. The Login page should open if you are connected to the home networking modem.
3. Type “admin” in the Username field and the “pre-shared key listed on the bottom of the modem” in the Password field and press enter.
*** After logging in with the default login information, you may or may not be prompted to change the login password. If you are prompted to change it, you may be redirected to the login page after completion. Enter the Captcha and move to the next step of changing the network name and password or leaving them at default. ***
NOTE: If you are prompted and change the login password for the modem or choose to change it, there is no way to retrieve that password if it is forgotten. The modem will need to be reset to factory default settings by pressing the button, located in a small hole, on the back of the modem. Press and hold the button for at least 25-30 seconds to reset the modem. (Resetting the modem may also be useful for recurring issues like intermittent connectivity, slow internet, etc.)
CHANGING/ADJUSTING WIRELESS NETWORK SETTINGS
After logging into the modem, the initial page will be on “Gateway“. There will be some heading options on the left side of the login screen. Choose “Connection” drop down (heading) and then choose “Wi-Fi“. The 2.4Ghz and the 5Ghz options should be available. Select either one of those two options to go into the settings for that network.
There should be an option for “Wireless Channel“. Typically, this setting is set to Auto, but the channel can be manually adjusted as well. The recommended channels are 1, 6, and 11 for the 2.4ghz network because they don’t overlap each other. Overlapping of channels can cause interference on wi-fi. For the 5Ghz network, there will be similar options, except the channels are 36, 40, 44, 48 (lower channels) and 149, 153, 157, 16x, etc. (higher channels). Most newer devices are, usually, able to see the 5ghz network. Out of those devices, some may not be able to see the higher 5ghz channels. In that instance, adjusting the 5ghz channel to the lower channels may be necessary.
Also, keep in the mind that the “Channel Bandwidth” may be adjusted as well for the 2.4Ghz and 5Ghz bands. For the 2.4Ghz, the options are typically 20 and 20/40. If there are a lot of networks visible, then using the 20Mhz only, is recommended. For the 5Ghz, the options are 20, 20/40 and 20/40/80. If there are a lot of networks visible, then using 20/40 or 20Mhz only is recommended for the 5Ghz, depending on how many. If there are hardly any networks visible, then 20/40/80 may be used, unless you start having issues with connectivity and/or speed on wi-fi. That’s one of settings that may be adjusted, along with the wi-fi channel and wi-fi mode. Please see the screenshots below.
INITIAL LOGIN SCREEN
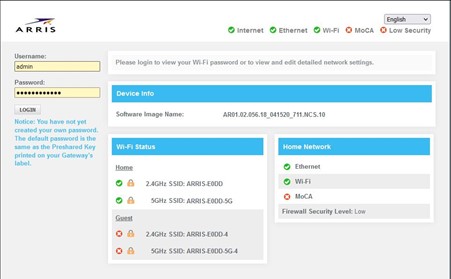
AFTER LOGIN – By selecting the Network name for the 2.4 and 5ghz, you can change the name and password of the wi-fi network.
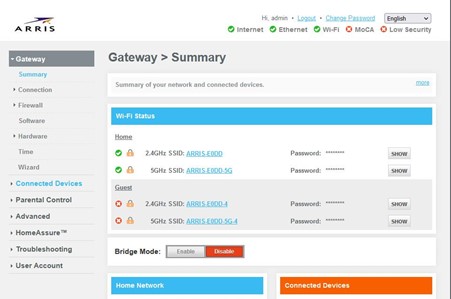
WI-FI SETTINGS – Select the “Connection” option and then select Wi-Fi to see the 2.4 and 5ghz networks.
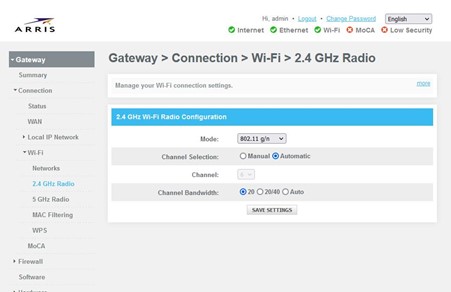
2.4Ghz – The wireless mode, channel and channel bandwidth may be adjusted to assist with wi-fi performance. For the “Wireless Mode”, B/G/N options are available. “B” and “G” are older standards for the 2.4ghz network. Most, if not all current devices are able to connect to the “N” standard. Set the mode to “N” only and the wi-fi will not be searching for the older “B” and “G” standard. That may also help with wireless performance issues. ( Refer to “Changing/Adjusting Wireless Network Settings” for the other options.)
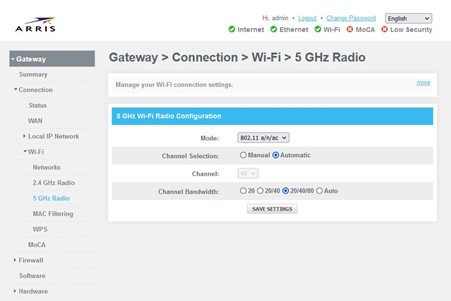
5Ghz – The wireless mode, channel and channel bandwidth may be adjusted to assist with wi-fi performance. For the “Wireless Mode”, A/N/AC options are available. “A” is an older standard for the 5ghz network. Most, if not all current devices are able to connect to the “N” and “AC” standard. Set the mode to “N/AC” and the wi-fi will not be searching for the older “A” standard. That may also help with wireless performance issues. ( Refer to “Changing/Adjusting Wireless Network Settings” for the other options.)
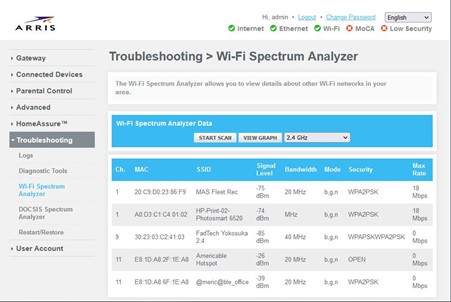
SPECTRUM ANALYZER – By selecting the “Troubleshooting” option you may be to view the “Wi-Fi Spectrum Analyzer”. Here, you can scan the other wireless networks around you for the 2.4 and 5ghz bands. This can help in determining the best channel for your wi-fi network. The “Signal Level” indicates how far away (the distance) another network is compared your own. (Ex. -75dB is further away; -39dB is closer)